What is Fresh Embryo Transfer? Everything You Need to Know
Choosing the right path in your fertility journey can feel challenging, especially when every week seems so important. You may find yourself scrolling forums, comparing clinic leaflets, and wondering which treatment will benefit you the most.
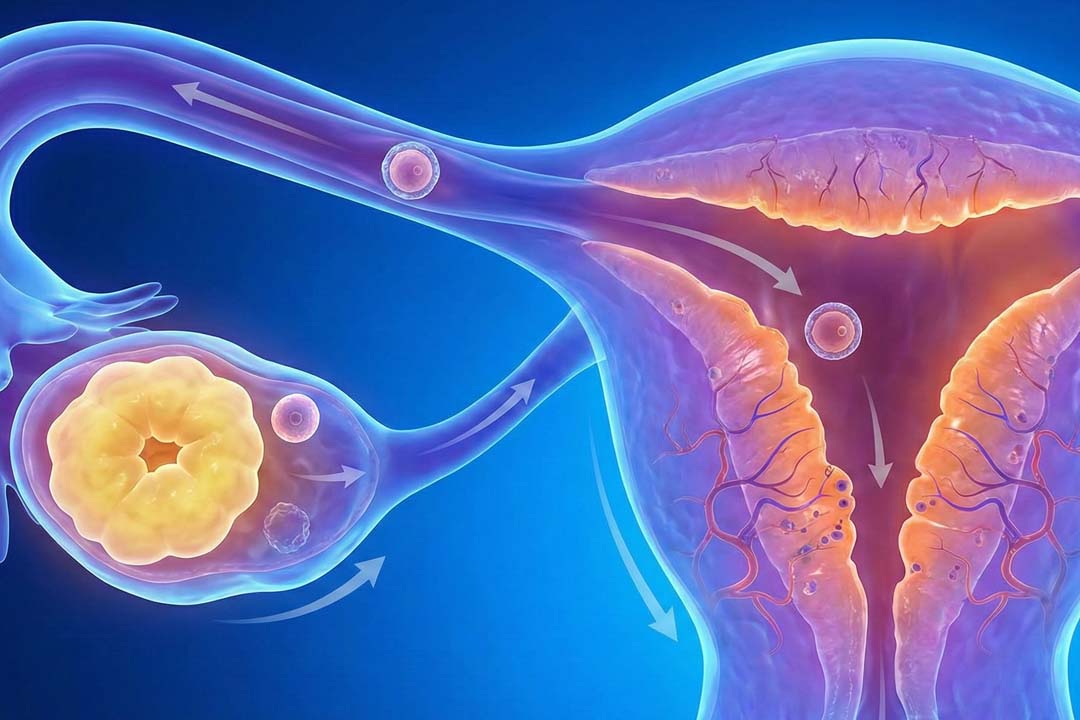
One term you will meet early is fresh embryo transfer. This is the process when an embryo formed in the lab is placed back into your uterus in the very same cycle the eggs were collected.
Because your hormone cycle is already modified, the uterine lining is naturally receptive, and that perfect timing makes the process feel like one continuous flow.
This guide will be helpful to explain how a fresh transfer works, what the numbers really mean, and what you can do to give yourself the best chance of success.

What is a Fresh Embryo Transfer?
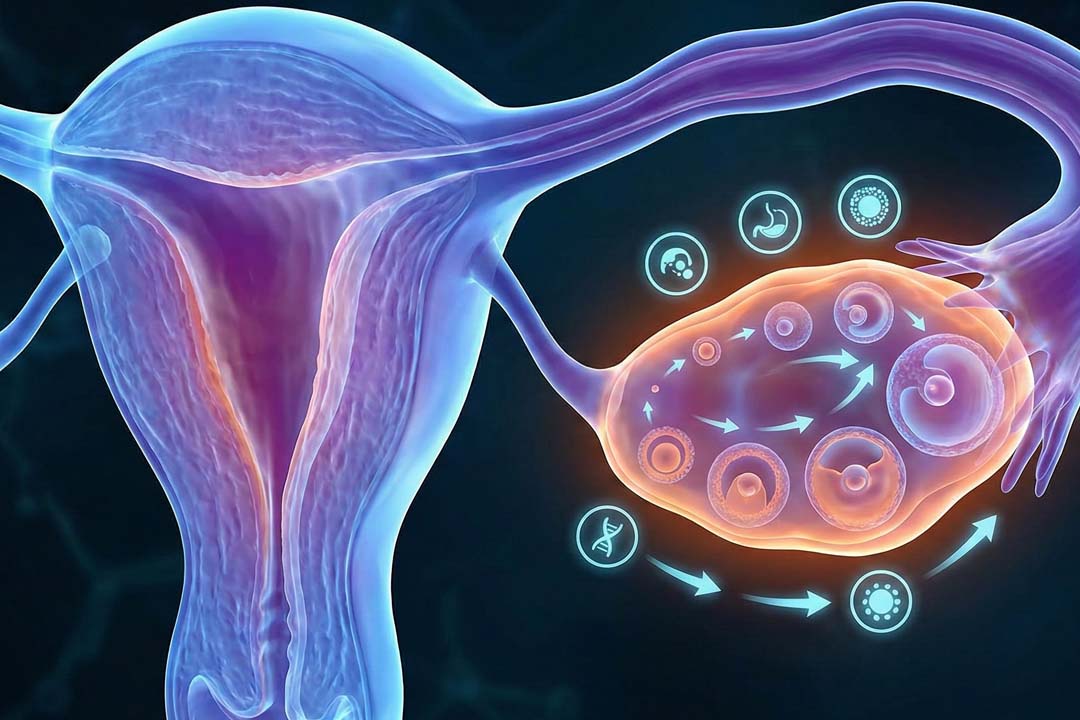
A fresh embryo transfer places a lab-fertilised embryo into the uterus during the same ovarian-stimulation cycle in which the eggs were retrieved.
The embryo is cultured for two to five (sometimes six) days, then transferred without being frozen.
The aim is to match the embryo’s development stage with the short “implantation window” of the uterine lining so it can begin settling in right away.
Why choose a fresh transfer?
Fresh embryo transfer has the following benefits:
- Speed: no need to wait for another cycle.
- Cost: you avoid freezing and storage fees.
- Continuity: many people like finishing the journey they started that month.
How does the Fresh Embryo Transfer Procedure Work?
The transfer itself is brief and usually painless. You lie on a gynaecology table while a thin catheter, loaded with the embryo in a droplet of culture fluid, is guided through the cervix under ultrasound.
The embryo is gently released, the catheter is withdrawn, and you rest for a few minutes before heading home.
Behind that simple moment is carefully timed steps:
- Ovarian stimulation: daily hormone injections grow multiple follicles.
- Trigger shot: an hCG or GnRH agonist injection matures the eggs.
- Egg retrieval (Day 0): eggs are collected under light sedation.
- Fertilisation: eggs meet sperm via conventional IVF or ICSI.
- Embryo culture (Days 1-3/5/6): embryos are graded for cell number, symmetry, fragmentation and, if cultured longer, blastocyst quality.
- Embryo selection: the best embryo (or occasionally two) is chosen.
- Transfer: typically on Day 3 (cleavage stage) or Day 5 (blastocyst).
- Luteal support: progesterone keeps the lining receptive.
- Pregnancy test: a blood hCG check 10–14 days later confirms implantation.
What is the Fresh Embryo Transfer Protocol?
Although clinics can change some details, a classic protocol looks like this:
- Controlled ovarian stimulation with FSH or hMG plus a GnRH antagonist.
- Trigger with hCG when lead follicles hit 18–20 mm.
- Progesterone begins within hours of retrieval to prime the lining.
- Single embryo transfer if embryo quality is excellent, reducing twin risk.
- Soft catheter and abdominal ultrasound guidance for precise placement.
- Post-transfer rest for only 10–15 minutes; extended bed rest adds no benefit.
- Light daily activities like walking, office work can resume the same day.
How successful is a fresh embryo transfer?
Live-birth rates, not just positive tests give the clearest picture. In women under 35, a fresh transfer leads to a baby roughly 40 %–45 % of the time. Success falls to about 35 % at ages 35–37, 25 % at 38–40, and under 10 % after 42.
Embryo grade, uterine health, and lifestyle habits can push those numbers up or down. A single top-grade blastocyst transferred fresh in good-prognosis patients often matches frozen results in the same age band.
What Helps Fresh Embryos Transfer Success?
Certain factors can help to increase the success rates of fresh embryo transfer, for example:
- High-grade embryo
- Optimal lining of 8–12 mm thickness with a trilaminar pattern
- Balanced hormones help in steady progesterone and oestrogen levels
- Healthy weight like a body-mass index between 19 and 30 helps implantation.
- Positive habits such as no smoking, limited caffeine, regular sleep, stress management.
- Quality lab environments like clean air, good culture media, and skilled staff nurture viable embryos.
Is a Frozen Embryo Transfer Better than a Fresh Transfer?
A frozen embryo transfer (FET) completed in a later cycle offers:
- Better endometrial control: the lining can be prepared in a calm hormonal setting.
- Lower OHSS risk: freezing avoids a pregnancy-related hCG surge that can worsen ovarian hyper-stimulation.
Large studies show fresh and frozen success rates are now broadly similar, with FET sometimes being ahead in high-responders or those with polycystic ovaries.
Fresh transfers, however, remain highly effective for many patients and deliver a faster time-to-pregnancy.
How Do You Prepare for a Fresh Embryo Transfer?
You can follow some simple measures to better prepare your body for the embryo transfer procedure:
- Stick to medication times
- Keep gentle exercise, such as walking or prenatal yoga, to support blood flow.
- Drink plenty of water to ease post-retrieval bloating.
- Limit caffeine and avoid alcohol.
- Take folic acid and clear any herbal supplements with your doctor.
Does a Day-6 Fresh Embryo Transfer make a Difference?
A Day-6 blastocyst took an extra 24 hours to reach full expansion. Clinics may transfer it fresh if the lining remains receptive.
While implantation rates run slightly lower than Day-5 transfers, many Day-6 embryos still yield healthy pregnancies.
What Does a Fresh Embryo Transfer Feel Like?
Most people liken it to a routine Pap smear. Expect mild pressure from the speculum and a brief cramp as the catheter passes the cervix.
From entering the room to walking out rarely takes more than twenty minutes, and normal activities can resume the same day.
Common Myths about Fresh Embryo Transfers
Myth: “I must stay in bed for days.” Light movement is safe and may aid circulation. Myth: “Eating pineapple guarantees implantation.” No food can override embryo genetics or lining health.
Myth: “Transferring two embryos always doubles success.” It mainly doubles twin risk.
Myth: “Fresh transfers are old-fashioned.” Advances in lab culture keep fresh success rates high.
What happens after a Positive Pregnancy Test?
If your blood hCG is positive, congratulations! You have the first sign of implantation. Your clinic will repeat the test after two or three days to confirm rising hormone levels.
Around Week 6 or 7 of pregnancy, you will have an ultrasound to look for a gestational sac and heartbeat.
Once viability is confirmed, routine care begins like any naturally conceived pregnancy.
Progesterone support may continue until Weeks 9–10 to stabilise the lining, after which prenatal vitamins, regular check-ups, and healthy habits take centre stage.
Conclusion
A fresh embryo transfer blends advanced laboratory science with the natural rhythm of your own body. You can influence many variables by taking medications on time, eating nourishing foods, moving your body, and taking good care of yourself each day.
If setbacks arise, remember that modern medicine offers several ways like freezing surplus embryos, adjusting stimulation doses, or scheduling a frozen transfer later.
Many live births from IVF come after more than one attempt. The journey can be demanding, yet it carries the promise of profound joy. Keep asking questions, keep advocating for your needs, and let each careful step guide you closer to the family you imagine.
Frequently Asked Questions
I’m 30. Is IVF with a fresh transfer—right for me?
If you have blocked tubes, severe male-factor infertility, or have tried other treatments without success, IVF with a fresh transfer offers strong pregnancy rates in your age group.
Can I request two embryos to improve my chances?
You can, but transferring two increases the risk of twins and complications. Many clinics suggest a single top-grade embryo instead.
Does bed rest help implantation?
Evidence shows routine light activity poses no harm and may even improve blood flow. Extended bed rest is unnecessary.
Will I feel implantation?
Most people feel nothing. Mild cramping or spotting can happen but are not reliable indicators. How soon can I travel?
Short car rides are fine immediately. Many clinics suggest waiting 48 hours before flying.
Is the medication schedule different if I choose a frozen transfer later?
Yes. In a frozen cycle, oestrogen and progesterone usually come from pills or patches, allowing more flexible timing.
Can diet affect implantation?
A balanced diet rich in protein, leafy greens, and healthy fats supports hormone production and tissue repair. Extreme diets are discouraged.
What happens to extra embryos?
Good-quality embryos not used in a fresh transfer are typically frozen for future attempts or sibling pregnancies.
Is age more important than all other factors?
Age matters, but embryo quality, uterine health, and lifestyle can offset some age-related decline, especially in your mid-thirties.
Are there gentler stimulation protocols?
Yes. Mild-stimulation regimens use lower drug doses yet still yield enough eggs for a fresh transfer.
About Us
AKsigen IVF is a premier center for advanced fertility treatments, with renowned fertility experts on our team. Specializing in IVF, ICSI, egg freezing, and other cutting-edge reproductive technologies, AKsigen IVF is committed to helping couples achieve their dream of parenthood. With personalized care and a patient-first approach, AKsigen IVF provides comprehensive fertility solutions under one roof.