Embryoscope and Its Role in IVF Treatment
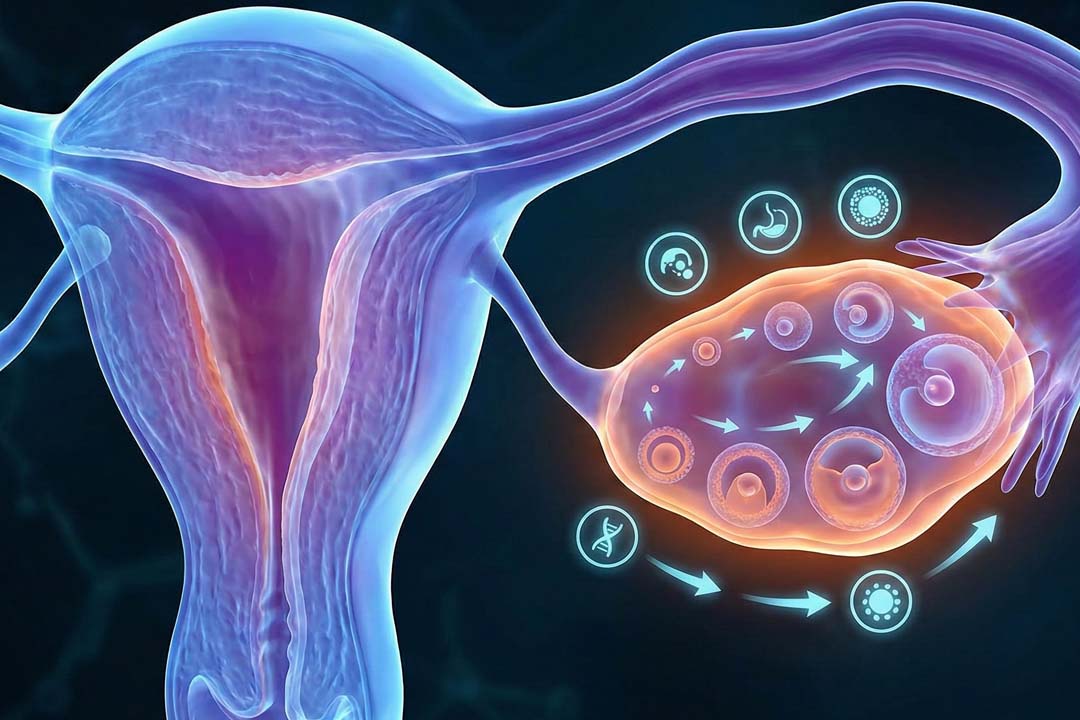
In vitro fertilization (IVF) has helped millions of couples to conceive, yet success still depends on one fragile stage: the first few days after the egg and sperm are fertilized.
During this window the embryo must grow in a lab dish, away from the body’s protective womb. Any fluctuation in temperature, light, or handling can reduce its chances of thriving.
That is where the Embryoscope, which is a next-generation time-lapse incubator, steps in. The device keeps embryos in a constant, womb-like setting by letting specialists watch each cell division without ever lifting the culture dish.
We’ll discuss what the Embryoscope does, how it differs from standard incubators, and why its round-the-clock monitoring is changing IVF outcomes for hopeful parents like you.

What Is an Embryoscope?
The Embryoscope is a high-tech incubator that photographs embryos every few minutes so they never need to leave their controlled environment.
Traditional incubators simply keep embryos warm. In contrast, an Embryoscope pairs that warmth with a tiny built-in camera and a light-safe imaging system. As the embryo divides from one cell to two, four, eight, and beyond, the camera snaps a picture.
Software then makes those images into a time-lapse movie. Because the dish stays sealed, carbon-dioxide and oxygen levels remain steady, mirroring the fallopian tube and uterus.
This blend of constant conditions and visual records helps embryologists judge quality without risking disturbance.
How Does the Embryoscope Differ From Conventional Incubators?
Under standard care, lab staff must open the incubator several times a day, pull each dish into room air, place it under a microscope, jot down observations, and return it. Even quick trips can trigger temperature drops and pH swings.
The Embryoscope eliminates those extra steps. All assessment happens on-screen, while the dish stays sealed. Fewer door openings mean a calmer internal climate, and the continuous film offers more data points than a once-a-day snapshot ever could.
Why Is a Stable Environment So Important for Early Embryos?
Because embryos are sensitive to even tiny shocks, and each shock affects their vitality. In the first week after fertilization, embryonic cells are busy copying DNA and laying down future organs. They have no spare energy to correct errors triggered by shifts in heat or acidity.
A two-degree Celsius drop or a quick pH rise can slow cell division or cause uneven cleavage. Over time that damage shows up as lower implantation rates or higher miscarriage risk.
Embryoscope shields embryos from these micro-stressors and gives each cell cycle a smoother run.
How Does Time-Lapse Imaging Work Inside the Embryoscope?
The system uses low-intensity, embryo-safe light to capture images without harming development.
A ring of LEDs emits gentle light through the culture dish. The camera beneath records images at preset intervals—often every 10–15 minutes. Sophisticated algorithms then align the frames, creating a detailed movie of growth milestones.
Because the light is both brief and wavelength-filtered, it avoids generating heat or reactive oxygen species. Meanwhile, the software can detect any abnormal timing, such as delayed second cleavage so embryologists can grade embryos more precisely.
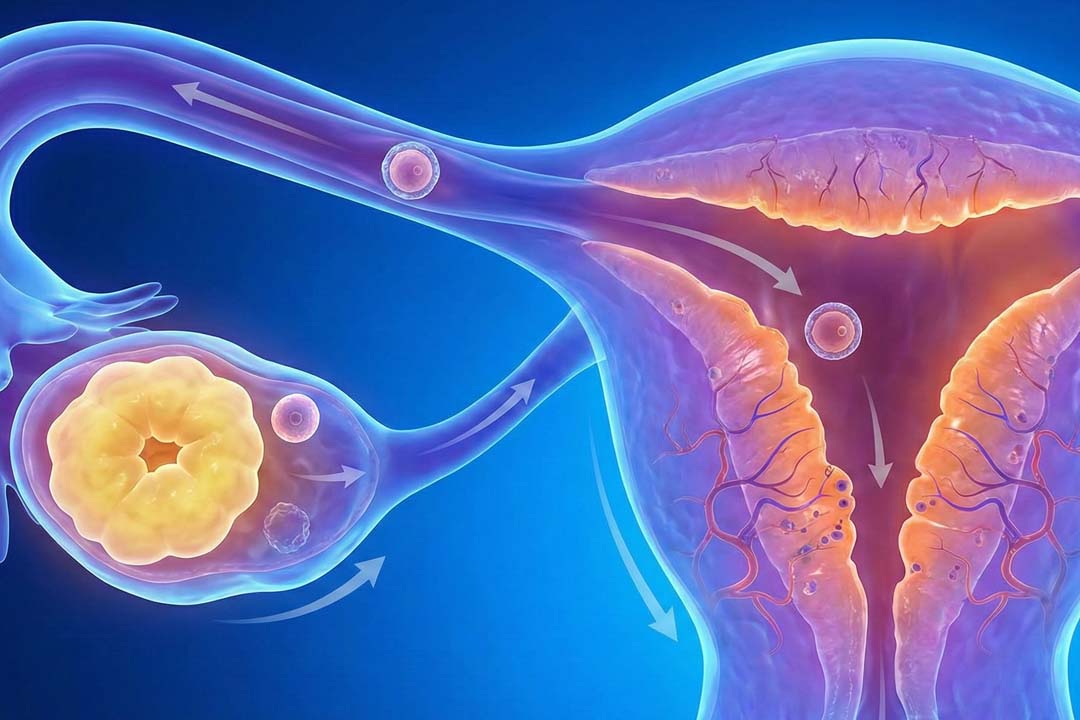
When During IVF Is the Embryoscope Used?
From fertilization until the day of transfer which is usually five to seven days. Once eggs are retrieved and combined with sperm, each resulting zygote is placed into an Embryoscope chamber.
Over the next week, the time-lapse system runs nonstop, storing thousands of frames per embryo.
On day three and day five, clinicians review the movies, pick the embryo (or embryos) with the most regular development, and schedule transfer or freezing. Because the dish never leaves the unit, even the selection process keeps conditions intact.
Does the Embryoscope Improve IVF Success Rates?
Many clinics report higher implantation and live-birth rates when they add time-lapse monitoring. Researchers attribute the gain to two linked factors:
- First, constant culture conditions mean fewer embryos are arrested in early cleavage, leaving a larger pool of healthy options.
- Second, time-lapse movies reveal subtle irregularities like direct three-cell jumps or cytoplasmic fragmentation so staff can spot hidden weaknesses that a quick microscope glance might miss.
Studies comparing matched cycles have shown pregnancy rates rising by roughly 10–15 percent when Embryoscope selection replaces traditional checks. While numbers vary by clinic and patient age, the overall trend is upward.
Who Might Benefit Most From Embryoscope Monitoring?
Couples with limited embryos or previous IVF failures often gain the biggest advantage. If you produce only a few embryos in a cycle, choosing the single most viable one becomes critical. Time-lapse will help narrow that choice.
Similarly, people who have faced repeated implantation failure may have embryos that look fine on day three but develop issues later.
Continuous imaging catches such late-stage problems. Patients using donor eggs, pursuing elective single-embryo transfer, or carrying known genetic risks can also profit from the added insight.
Are There Any Drawbacks or Limitations?
There are few limitations of embryoscope monitoring, they are as follows:
- The main downsides are cost and the fact that imaging cannot fix genetic issues.
- Embryoscope systems are expensive, and clinics pass part of that cost to patients.
- Not every center owns one, and availability may depend on location.
- Viewing a time-lapse cannot correct chromosomal errors such as trisomies; it only helps identify embryos more likely to be normal.
- Some embryos that look flawless still carry genetic faults, which is why pre-implantation genetic testing (PGT) may be offered alongside Embryoscope monitoring for high-risk cases.
How Do Clinics Select Embryos Without an Embryoscope?
They briefly remove dishes from a standard incubator and check cells under a microscope. This traditional approach still works and leads to healthy births worldwide.
Embryologists look at cell number, symmetry, and fragmentation at set time points, usually day three and/or day five.
After each inspection, dishes return to the incubator as quickly as possible. The method’s weakness lies in its nature because any abnormal event occurring between checks goes unseen. The Embryoscope fills that gap by filming continuous development.
Is the Embryoscope Worth the Additional Cost?
For many couples, the chance of fewer cycles and faster pregnancy offsets the fee. Time-lapse monitoring can reduce the number of transfers needed to achieve a live birth, saving both emotional strain and overall expenses.
If one extra set of images pushes success from the second cycle to the first, the savings in medication, time off work, and stress may far exceed the Embryoscope surcharge.
Ultimately, the decision is personal. Asking the clinic for its specific success statistics can help you weigh value against budget.
Conclusion
The Embryoscope represents a quiet revolution in embryo care. It keeps the delicate first week of life shielded from outside shocks while giving specialists a detailed roadmap of each division by combining precise environmental control with unobtrusive time-lapse imaging.
For you and your partner, that can translate into clearer choices, fewer transfers, and a smoother journey toward pregnancy.
Though it cannot heal genetic defects or remove all uncertainty, the Embryoscope helps the odds in favor of a healthy embryo finding its home in the uterus.
If you’re considering IVF, ask your clinic about its culture systems, success statistics, and whether time-lapse monitoring could make a meaningful difference in your personal path to parenthood.
Frequently Asked Questions
I’m 30-Is IVF right for me, or should I try other treatments first?
If you’ve tried to conceive naturally for a year (or six months if you’re over 35) without success, it’s reasonable to speak with a fertility specialist. At 30, many people still respond well to lifestyle changes or simpler treatments like ovulation induction or intrauterine insemination. However, if male-factor infertility, blocked tubes, or severe endometriosis is present, IVF may offer the most efficient path.
Is the Embryoscope safe for embryos?
Yes. The imaging system uses low-intensity, embryo-safe light and keeps temperature, pH, and gas levels stable. Numerous studies show no increase in birth defects or developmental delays compared with conventional incubators.
Can the Embryoscope guarantee pregnancy?
No incubator, however advanced, can promise a baby. The Embryoscope improves selection and protects embryos, but factors like uterine health, genetics, and overall well-being still influence outcomes.
Does time-lapse monitoring replace genetic testing?
It helps but does not replace PGT. The Embryoscope spots developmental timing issues, while PGT directly analyzes chromosomes. Together they offer a clearer picture, yet each addresses different risk areas.
How long can embryos stay in the Embryoscope?
Most labs culture embryos up to day seven. After that, the embryo either gets transferred, frozen for future use, or, if it has not reached the blastocyst stage, is usually discarded according to clinic policy.
Can we watch the embryo movies ourselves?
Many clinics share selected clips during consultations or after transfer. Viewing the early life of your potential child can be inspiring, though policies differ, so ask your care team.
Studies comparing matched cycles have shown pregnancy rates rising by roughly 10–15 percent when Embryoscope selection replaces traditional checks. While numbers vary by clinic and patient age, the overall trend is upward.
About Us
AKsigen IVF is a premier center for advanced fertility treatments, with renowned fertility experts on our team. Specializing in IVF, ICSI, egg freezing, and other cutting-edge reproductive technologies, AKsigen IVF is committed to helping couples achieve their dream of parenthood. With personalized care and a patient-first approach, AKsigen IVF provides comprehensive fertility solutions under one roof.