Fertility After 40: Chances, Challenges, and Treatment Options
If you’re exploring pregnancy in your forties, you’ll see lots of numbers and headlines. Fertility does decline with age, but good pre-conception care, realistic timelines, and appropriate treatment (when needed) can make a real difference.
This article breaks down what changes biologically after 40, the real-world odds, health considerations for pregnancy, practical steps to improve your chances, and when treatments like IUI, IVF, or donor eggs may help.
What Actually Changes with Age?
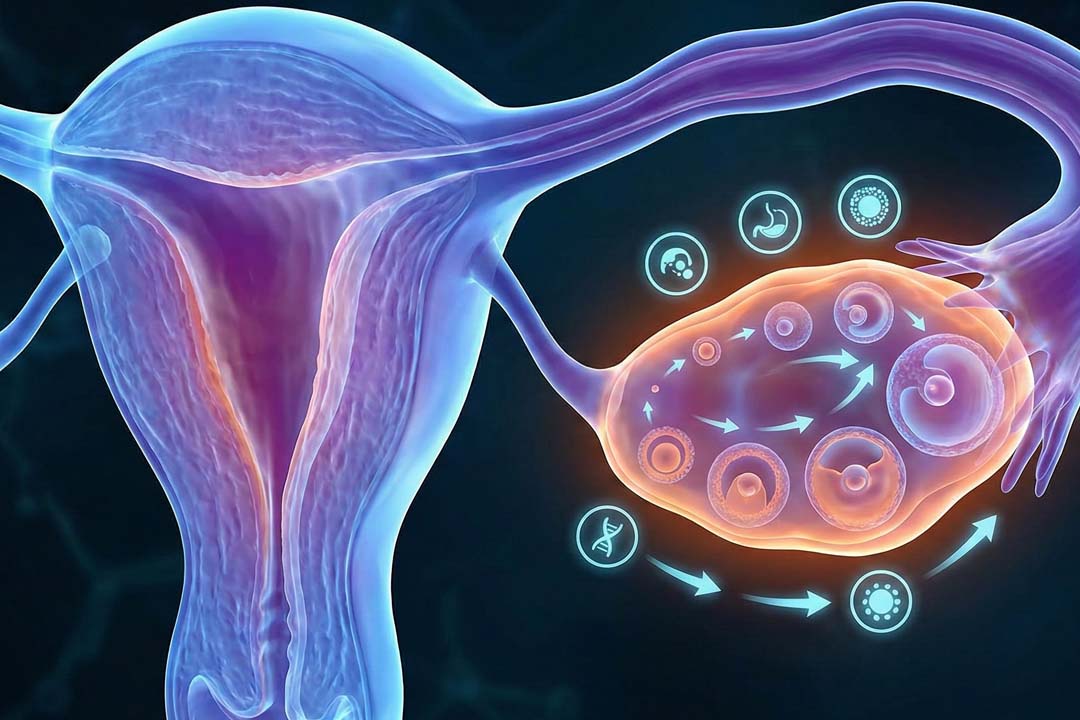
Egg number and egg quality fall with time, and that’s the main reason natural fertility declines in your 40s.
You’re born with a finite ovarian reserve (your lifetime supply of eggs). That pool declines steadily, then more steeply after the late 30s. Modelling of ovarian reserve suggests a pronounced acceleration in depletion around age 37, which helps explain the sharper fertility drop in the early 40s. Fewer eggs means fewer opportunities for a chromosomally normal egg to ovulate and implant.
Egg quality also changes. Chromosomal errors (aneuploidy) in eggs rise with age, which is why miscarriage and certain chromosomal conditions become more common later in life. Professional bodies note that relative fertility at age 40 is roughly half that of people in their late 20s to early 30s, when fertility peaks.
Fertility After 40 Statistics
The chance of pregnancy per menstrual cycle at 40 is small (often quoted at under 5% per cycle), and miscarriage risk rises to roughly one-third or more.
Monthly chances: Data summarized by fertility organisations show natural conception odds at age 40 are typically <5% per cycle (compared with ~20–25% in the 20s). Remember, these are averages, not guarantees for any one person.
Miscarriage risk: By age 40, ~33–40% of recognized pregnancies miscarry, mostly due to chromosomal abnormalities.
Chromosomal conditions: The risk of a Down syndrome birth rises from about 1 in 1,480 at age 20 to ~1 in 85 by age 40; by 45 it is roughly 1 in 35.
It’s equally important to note that many people in their 40s do have healthy pregnancies and babies, especially with mindful prenatal care and timely support.
Health and Pregnancy Risks After 40
Risks are higher than in the 20s and 30s, but most can be managed with careful antenatal care and timely decisions.
- Compared to younger ages, pregnancies after 40 carry higher odds of gestational diabetes, preeclampsia (pregnancy-induced high blood pressure), placenta previa, preterm birth, and cesarean delivery.
- Large studies and consensus statements confirm these patterns. The absolute risks for any one person can still be moderate, and modern monitoring aims to detect problems early.
- Some services recommend closer surveillance late in the third trimester because the stillbirth risk rises with advancing age, particularly nearing due dates; policies vary by country and care setting. Discuss timing of delivery with your clinician as you approach the term.
- Sperm quality can also decline over time (motility, DNA fragmentation), and some conditions are more frequent with older paternity, though these effects are generally less abrupt than changes in egg quality.
How to Improve Fertility After 40
You can’t change egg age, but you can meaningfully improve overall chances by optimizing timing, health, and when to seek help.
Get a pre-conception health check
Review blood pressure, thyroid function, and diabetes risk; update vaccines; screen for STIs; and discuss medications. This reduces preventable obstacles to conception and early pregnancy risks.
Time intercourse with ovulation
Use luteinizing hormone (LH) urine kits or track cycle length and cervical mucus; aim for sex every 1–2 days during the fertile window (the five days before ovulation and ovulation day). Fertility societies emphasize timing as the biggest “free” booster.
Lifestyle Upgrades that Actually Matter:
- Stop tobacco and avoid vaping or marijuana as both impair fertility.
- Moderate alcohol and keep caffeine ~200 mg/day or less while trying to conceive.
- Aim for a healthy BMI through a balanced diet and regular exercise to improve ovulation and reduce gestational risks if pregnancy occurs.
Know When to Seek HelpIf you’re 40 or older, most guidelines suggest seeking evaluation after 6 months of trying (or sooner if cycles are irregular, there’s known endometriosis, fibroids affecting the cavity, or male-factor issues).
How to Boost Your Fertility After 40?
Focus on precise timing, optimize health, and get an early, targeted evaluation; if needed, move to effective treatments without long delays.
Why this matters: at 40+, time is the scarcest resource. Quick identification of treatable factors (thyroid problems, tubal issues, semen parameters) and prompt access to options such as ovulation induction, IUI, or IVF preserves precious cycles and can markedly increase the odds compared with “wait and see.”
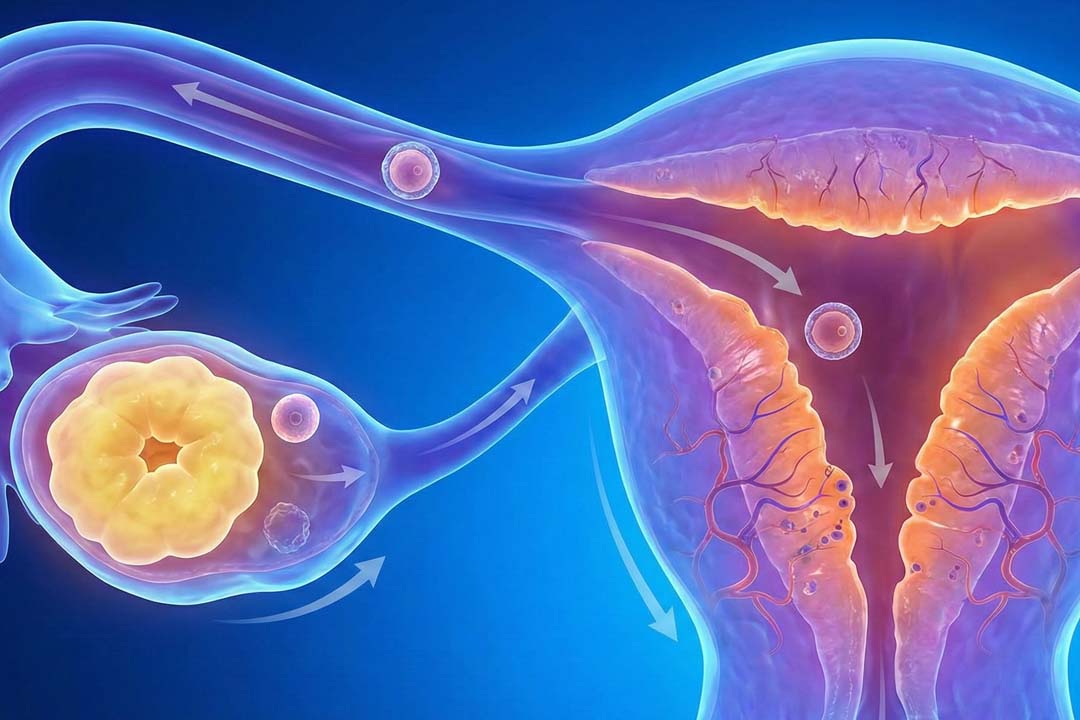
Fertility Treatment After 40
Success with your own eggs declines with age; donor eggs can largely overcome egg-age effects. Use success-rate tools and individual medical advice to choose wisely.
- IUI (intrauterine insemination): Often considered when sperm parameters are mildly suboptimal or when ovulation induction is used. Per-cycle success is modest and further limited after 40, so many clinicians recommend moving to IVF sooner if feasible. (General consensus reflected across guidelines and reviews.)
- IVF with your own eggs: National datasets show live-birth rates fall substantially in the early 40s. Planning may include PGT-A (chromosome screening) to avoid transferring embryos with aneuploidy, though this does not create healthy embryos but it helps select among those made. Success-rate calculators from professional registries help set expectations.
- IVF with donor eggs: Because egg quality tracks the donor’s age, donor-egg IVF can restore higher success probabilities for recipients over 40, often in the 40–55% per-transfer range in large contemporary series (clinic-to-clinic variation exists).
NOTE: Try not to invest many months in lower-yield approaches if testing suggests limited ovarian reserve. Discuss timelines early so you can pivot efficiently.
Pregnancy Care After 40
Individualized antenatal plans help manage higher-than-average risks. Expect more frequent visits, diabetes screening, blood-pressure checks, and third-trimester growth and well-being assessments. Some care pathways consider earlier delivery for older mothers due to a rising stillbirth curve late in the third trimester; policies differ by region, so follow local guidance.
Women’s Fertility After 40 vs. Partner Factors
Egg age is the main driver, but partner age and health matter too. Research shows sperm motility and morphology tend to decline with age, and DNA fragmentation can rise, these factors may lengthen time to pregnancy and carry implications for offspring health risks. Lifestyle changes (weight, sleep, smoking cessation), controlling chronic disease, and addressing treatable male-factor issues can help.
Cost of Fertility Treatment After 40
The cost of fertility treatment after 40 can vary, but a single cycle of In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) in India may range from approximately ₹1.5 lakh to over ₹5 lakh, depending on the specific clinic and treatment required.
Other treatments like Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) are less expensive, costing around ₹17,600 to ₹22,000 per cycle. Additional expenses might include preimplantation genetic testing, embryo freezing, and donor services, which will increase the total cost.
How to Plan for Pregnancy in Your 40s?
If you follow proper guidelines, the chances of having a baby even in your 40s can become higher, for instance:
- Start with clear information: Understand that monthly conception odds are lower at 40+, and miscarriage risk is higher but also that many pregnancies proceed safely with good care.
- Act early and efficiently: Time intercourse precisely for several months, then seek evaluation without delay if pregnancy hasn’t happened. Use that information to choose the most effective next step for you.
- Plan for pregnancy care: Once pregnant, expect closer monitoring for diabetes, blood pressure disorders, and placental issues; these steps are about prevention and early action.
- Consider treatment pathways: If ovarian reserve is significantly reduced, discuss whether moving straight to IVF (with or without donor eggs) is the best path to a healthy live birth. Use national data tools to set expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to improve fertility after 40 without jumping straight to IVF?
Use LH kits to catch the surge, have sex during the fertile window, start prenatal vitamins, and address thyroid, prolactin, or insulin resistance if present. If there’s no pregnancy after 6 months (or sooner with red flags), move to structured treatment discussions.
Is IUI worth trying at 40?
IUI can help when ovulation induction is needed or when semen parameters are mildly reduced, but per-cycle success is modest after 40. Your doctor may recommend limiting IUI attempts (e.g., up to 2–3 cycles) before pivoting to IVF if egg reserve is low.
What are realistic IVF expectations at 40–42 with my own eggs?
Success rates are lower than in the 30s, but vary by individual. Calculators based on national data can personalize estimates. Registry tools summarize age-specific odds and cumulative success across multiple cycles. Discuss lab quality, single-embryo transfer, and whether PGT-A fits your case.
Conclusion
Fertility after 40 is a real but navigable challenge. Age lowers the number and quality of eggs, which reduces monthly conception odds and raises miscarriage risk, yet many people still have healthy pregnancies with good preparation and timely care. The most effective approach is simple and focused: optimize health (sleep, nutrition, weight, no tobacco, limited alcohol), time intercourse precisely using ovulation tracking, and seek an evaluation within six months of trying (earlier with irregular cycles or known issues).
About Us
AKsigen IVF is a premier center for advanced fertility treatments, with renowned fertility experts on our team. Specializing in IVF, ICSI, egg freezing, and other cutting-edge reproductive technologies, AKsigen IVF is committed to helping couples achieve their dream of parenthood. With personalized care and a patient-first approach, AKsigen IVF provides comprehensive fertility solutions under one roof.