Ovulation Induction in PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common reasons periods become irregular and ovulation goes off-schedule. When the ovaries don’t release an egg regularly, conceiving can take longer but targeted treatment can help.
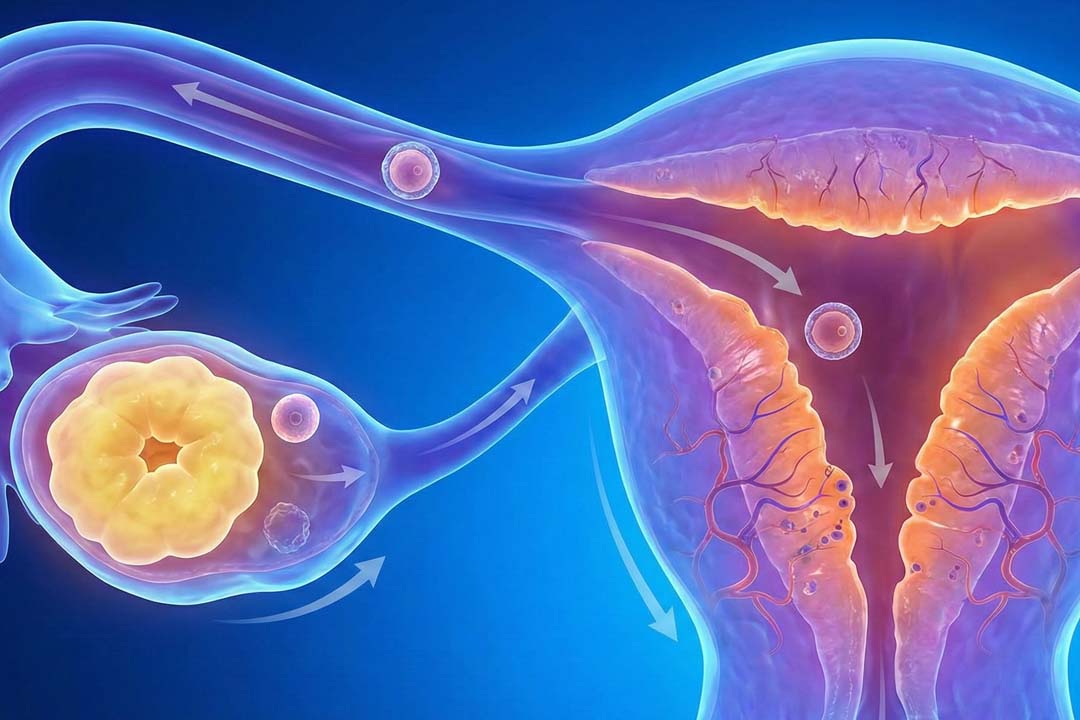
Ovulation induction simply means using medicines (and sometimes minor procedures) to nudge the ovaries into releasing one mature egg at the right time. Most people don’t jump straight to IVF for PCOS, they start with simpler, lower-risk steps that restore ovulation and time intercourse or intrauterine insemination (IUI).
Good pre-treatment checks, smart drug choice and careful monitoring make these cycles safer and more effective. Lifestyle measures such as sleep, movement, nutrition, weight management remain the foundation and can even bring back natural ovulation for some.
What Does Ovulation Induction Actually Do?
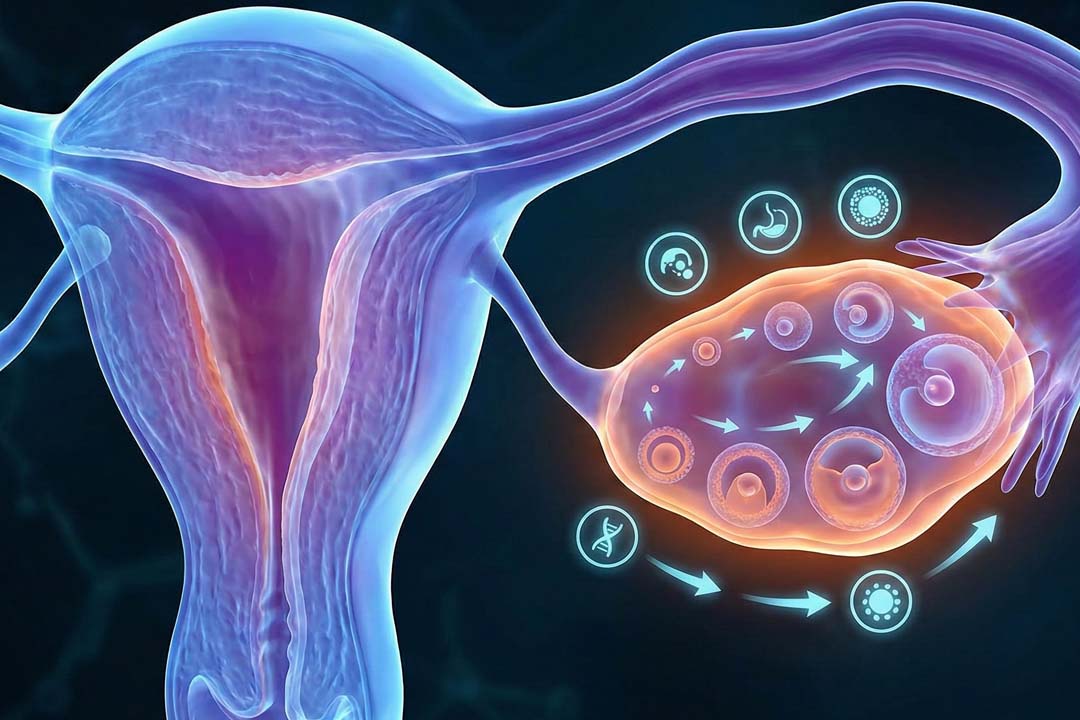
It encourages the growth and release of one egg in a cycle so conception can occur, while aiming to avoid too many eggs maturing at once. That’s why clinics monitor follicles on ultrasound and adjust doses to keep things safe and reduce the chance of twins or more.
PCOS alters hormone signals between the brain and the ovaries, often leading to infrequent or absent ovulation. Insulin resistance, higher androgens, and disrupted LH/FSH signaling all play a role, which is why both lifestyle steps and targeted medicines are used.
Which Tests are Required Before Ovulation Induction?
Yes, rule out other fixable reasons for anovulation and check overall fertility basics. Most people have an ultrasound of the uterus/ovaries and blood tests that typically include thyroid and prolactin; if either is off, correcting it can normalize cycles. It’s also standard to look at ovarian reserve (e.g., AMH, baseline FSH) to guide expectations, and to complete a semen analysis and consider a tubal patency check if history suggests it.
Where Does Metformin Do?
Metformin targets insulin resistance. It can restore more regular cycles in some and is often used alongside letrozole or clomiphene, especially when metabolic features are prominent. On its own, it’s generally less effective than letrozole/clomiphene for live birth, but it remains a useful adjunct and has broader metabolic benefits.
When are Gonadotropin Injections Used?
If oral medicines don’t trigger ovulation, low-dose FSH injections are the next step. Modern “low-and-slow” protocols begin around 37.5–75 IU daily, with tiny increases guided by ultrasound and (sometimes) estradiol levels.
The goal is monofollicular development; because the multiple-pregnancy risk is real with injectables, monitoring is essential and cycles may be cancelled if too many follicles emerge.
Triggering and timing: An hCG trigger mimics the natural LH surge; ovulation typically occurs 36–48 hours later, so intercourse or IUI is scheduled accordingly.
OHSS caution: Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is uncommon with oral agents but can occur with injectables; clinics use conservative dosing and monitoring to prevent it. ASRM
“Ovarian Drilling” (Surgical Option): When to Choose?
Laparoscopic ovarian drilling is not the first line. It’s considered mainly in clomiphene/letrozole-resistant cases, when access to monitoring is difficult, or when reducing the risk of multiple matters.
The procedure makes small cautery punctures on the ovarian surface to lower androgen production and “reset” ovulatory signaling. It can restore ovulation for many, but evidence for better live-birth than medical therapy is mixed, and it’s invasive. Adhesions (scar tissue) and a potential impact on ovarian reserve are the key risks, so it’s reserved for selected cases and performed with limited punctures/energy.
How Many Cycles Should I Try Before Changing Plans?
There isn’t a one-size answer, but in practice many try 3–6 ovulatory cycles with oral agents (within the clomiphene 6-cycle limit) before moving to injectables or considering IVF, with decisions shaped by age, ovarian reserve, semen analysis and tubal status.
What to Expect Ovulation Induction?
The process of ovulation induction include several steps:
- Ultrasound (“follicle tracking”) checks how many follicles are growing and their size.
- Hormone checks may include estradiol and mid-luteal progesterone to confirm ovulation.
- If too many follicles develop, cycles are paused or cancelled to lower multiple-pregnancy risk.
Practical Tips for Timing and Home Tracking
OPKs can be tricky in PCOS. Because baseline LH may be higher or erratic, simple urine LH kits may give misleading positives; clinics therefore rely on ultrasound and hormone tracking for precision.
The hCG “trigger shot” (when used) is your scheduling anchor: ovulation is expected ~36–48 hours later, so plan intercourse or IUI in that window.
Safety, Side Effects, and Reducing Risks
The heavy usage of drugs can sometimes lead to development of several symptoms, for example:
- Headaches
- Hot flushes
- Mood changes
- Vision changes with clomiphene are rare but important
- OHSS
Frequently Asked Questions
Is IVF the right next step if I’m 30?
Not automatically. If tubes are open and semen analysis is fine, many 30-year-olds with PCOS conceive with letrozole-induced ovulation (with or without IUI). IVF is usually considered after oral agents and, if needed, low-dose injectables have been tried, or if other factors (blocked tubes, severe male factor, very limited time) push you there sooner.
How many eggs should grow in a safe ovulation-induction cycle?
The aim is one mature follicle. More follicles raise the chance of twins or higher-order multiples, so clinics adjust doses or cancel if recruitment is excessive.
Will I always need an hCG trigger?
Not always. Some people ovulate on their own once a follicle matures; others benefit from an hCG trigger to nail the timing for intercourse or IUI. Ovulation is expected roughly 36–48 hours after the shot.
Is metformin enough by itself?
Sometimes it regularizes cycles, particularly with insulin resistance, but letrozole or clomiphene typically have better live-birth data. Many clinicians combine metformin with these when appropriate.
What’s the real risk of twins?
With oral agents, the twin risk is a few percent; with injectables, the multiple-pregnancy rate is significantly higher if many follicles develop. Careful dosing and ultrasound cut this risk.
Are there non-drug steps that truly help with PCOS?
Yes. Structured lifestyle measures like dietary tweaks, regular exercise, behavior support are first-line in PCOS and can restore ovulation for some, especially with about 5–10% weight loss. They also improve overall health during pregnancy.
Do OPKs work if I have PCOS?
They can be less reliable because LH can be high or surge multiple times. Ultrasound and progesterone checks are more dependable in PCOS-related induction cycles.
When should I think about IVF?
Consider IVF earlier if there are tubal problems, severe male-factor infertility, or if you’ve done several ovulatory cycles with oral/injectable medicines without success and time is a priority. Age, ovarian reserve and personal timelines shape this decision.
Conclusion
For PCOS, ovulation induction is usually a stepped plan: optimize lifestyle, start with letrozole (often the most effective first-line), consider clomiphene where appropriate, move to low-dose gonadotropins if needed, time ovulation with or without an hCG trigger, and reserve ovarian drilling for select, medication-resistant cases.
Close monitoring keeps you safe and minimizes multiples, while smart escalation avoids losing time. With the right sequence and support, many people with PCOS conceive without needing IVF.
About Us
AKsigen IVF is a premier center for advanced fertility treatments, with renowned fertility experts on our team. Specializing in IVF, ICSI, egg freezing, and other cutting-edge reproductive technologies, AKsigen IVF is committed to helping couples achieve their dream of parenthood. With personalized care and a patient-first approach, AKsigen IVF provides comprehensive fertility solutions under one roof.